Using faux leather in various applications requires understanding its specifications and testing standards. This article explores the essential tests to ensure strength, durability, and performance, guiding manufacturers and designers in selecting the right material.
Faux leather product specifications include tests for tear strength, tensile strength, flex resistance, abrasion resistance, stain resistance, colorfastness, flammability, and antimicrobial properties. These tests ensure the material meets necessary performance standards for various applications.
Let’s delve deeper into the key tests and their significance for faux leather products.

How Do You Test for Synthetic Leather?
Testing synthetic leather involves several methods to determine its authenticity and quality. One common test is the fire test: real leather chars and smells like burnt hair, whereas synthetic leather catches fire or melts, revealing its plastic origins. Such tests, while destructive, provide definitive proof of the material’s nature.

Key Tests and Specifications for Faux Leather
In the USA, faux leather product specifications often follow standards set by organizations like ASTM International. Key tests include:
- Tear Strength: Measures the force required to initiate and propagate a tear (e.g., ASTM D4705).
- Tensile Strength: Evaluates the maximum tensile force the material can withstand before breaking (e.g., ASTM D2208).
- Flex Resistance: Assesses the material’s ability to withstand repeated flexing without cracking (e.g., ASTM D2097).
- Abrasion Resistance: Determines the material’s resistance to surface wear (e.g., ASTM D3389).
- Stain Resistance: Evaluates the material’s ability to resist staining (e.g., ASTM D3690).
- Colorfastness: Measures resistance to color change (e.g., AATCC Test Methods).
- Flammability: Assesses fire resistance (e.g., ASTM E84).
- Antimicrobial Properties: Evaluates resistance to microbial growth (e.g., AATCC Test Method 100).

Several studies have evaluated the performance of faux leathers based on these tests, including:
- “Performance Evaluation of Synthetic Leathers for Automotive Upholstery Applications” by Nazan Avcu et al. (Journal of Coatings Technology and Research, 2019) [Link: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s11998-019-00238-z]
- “Flammability and Smoke Emission Characteristics of Artificial Leather” by Jian Zhang et al. (Journal of Fire Sciences, 2015) [Link: https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/10.1177/0734904115623706]
- “Antimicrobial Properties of Synthetic Leather” by Eman A. Radwan et al. (Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 2012) [Link: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/app.36891]
- “Evaluation of Faux Leather Upholstery Materials” by Katrina M. Heider et al. (Journal of Textile and Apparel, Technology and Management, 2010) [Link: https://ojs.cnr.ncsu.edu/index.php/JTATM/article/view/1190]
- “Characterization of Faux Leather: A Comparative Study” by Sanjukta Patra et al. (Journal of Coatings Technology and Research, 2018) [Link: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s11998-018-0087-y]
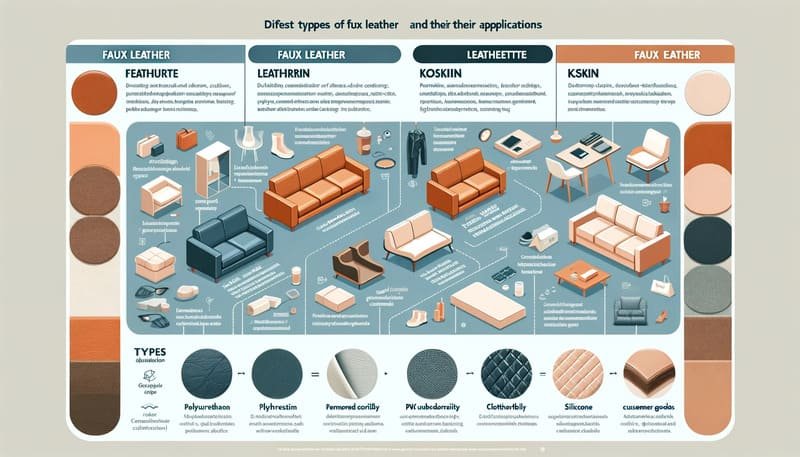
What Are the Different Types of Faux Leather?
Faux leather, also known by several other names such as leatherette and koskin, is used to describe various synthetic leather products tailored for specific applications:
- Faux Leather: Often used for sofa, chair, and headboard upholstery.
- Leatherette: Commonly used for auto upholstery and clothing.
- Koskin: Typically used for consumer goods.
There are three primary types of faux leather construction:
- Polyurethane (PU): Made from polyurethane, this type is soft and flexible.
- Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC): Known as vinyl, it is more durable and often used in tougher applications.
- Silicone: A newer type of synthetic leather, offering unique properties like high durability and environmental friendliness.
What Is High Quality Faux Leather?
High-quality faux leather, such as Ultraleather®, mimics the look and feel of the softest European calfskin. It offers superior strength, colorfastness, and a luxurious appearance, making it a preferred choice for premium applications.
What Material Is Used for Faux Leather?
Faux leather, also known as synthetic leather, begins with a fabric base such as polyester. The fabric is then given an imitation leather finish and texture with wax, dye, polyvinyl chloride (PVC), or polyurethane. This process creates a material that closely resembles genuine leather.
Does Faux Leather Have PFAS?
Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) are often found in various synthetic materials, including some types of faux leather. These chemicals are used for their stain-resistant and water-repellent properties but have raised environmental and health concerns due to their persistence in the environment and potential health risks.

Faux Leather vs PU Leather
Faux leather is a broader category that includes various synthetic leather types, while PU leather specifically refers to leather made from polyurethane. PU leather is generally softer and more flexible than other types of faux leather but may be less durable over time.
Understanding the specifications and tests for faux leather is crucial for ensuring its suitability for various applications. By considering these factors, manufacturers and designers can make informed decisions about material selection.


